Why Bottleneck Estimators May Lack Precision: My Reasons for Continuing Their Use

Why Bottleneck Estimators May Lack Precision: My Reasons for Continuing Their Use
Quick Links
- What Is a Bottleneck?
- What Bottleneck Calculators Promise to Solve
- Bottleneck Calculator Results Aren’t the Whole Story
- How to Use a Bottleneck Calculator Correctly
Key Takeaways
- Online bottleneck calculators are helpful but may not be 100% accurate.
- Program and game usage affect bottlenecks, not just the CPU and GPU.
- Utilize bottleneck calculators with real-world benchmarks for accurate hardware pairing.
Regardless of whether you’re new to PC building or have just been out of the game for a while, one of the hardest things to figure out is how to avoid a bottleneck. That’s when you might resort to online bottleneck calculators, but are these tools trustworthy?
What Is a Bottleneck?
In simple terms, a bottleneck describes a mismatch in performance between two PC components. The slowest component is the bottleneck. For example, if you have a powerful graphics card and a slow CPU, your CPU can’t deliver data fast enough to the graphics card. This means your graphics card is being held back by your CPU because it has to wait for new information to continue processing, which often leads to stutters, limited frame rates, and less-than-stellar overall performance.
Let’s use a quick analogy. Imagine a highway with four lanes with a section of the road under construction. Traffic is limited to only two lanes in that part, which leads to congestion. That part of the street practically slows down the entire highway to a crawl, which is what creates a bottleneck.

Justin Duino / How-To Geek
A similar thing can happen on your PC. Technically, any PC part could be a bottleneck. A motherboard that can’t provide stable power to your CPU slightly hinders its performance. A mouse with a low polling rate updates the cursor location less frequently. For the purposes of this article, we’ll focus on CPU and GPU bottlenecks , as they’re core components that affect performance the most.
What Bottleneck Calculators Promise to Solve
A bottleneck calculator is a tool that attempts to simplify identifying which piece of hardware is holding back your performance. A bottleneck calculator takes benchmark scores of each component and attempts to calculate the difference between the two to try to guess which component is holding the PC back and by how much.
Since they’re synthetic tools, they inherently can’t provide the same accuracy as a real benchmark. Also, they don’t take smaller factors into account, such as your RAM frequency and how it affects your CPU, storage type and speed, overclocking , PCIe versions , etc. Nonetheless, they’re an okay starting point for your build. It’s also worth noting that they tend to do a better job if you compare hardware that was released within the same year, as outdated benchmark data can skew the results.
Bottleneck Calculator Results Aren’t the Whole Story
The types of programs and games you typically run have a massive impact on how much of a bottleneck you have. For example, in CPU-intensive tasks that don’t require rendering graphics, such as compilation, the graphics card basically doesn’t matter.
Video games use the GPU more intensely, but the CPU utilization can range from 30% to 100%, depending on how many cores you have and how complex the video game logic is. Overwatch 2 uses less of your CPU than Starfield or Civilization V, for instance. This is something you should take into consideration, as a higher CPU bottleneck score could matter less if you only play multiplayer games. Screen resolution also has a big impact, as running the same graphics settings at a higher resolution will use significantly more GPU resources.
How to Use a Bottleneck Calculator Correctly
You can use a bottleneck calculator to get a rough idea of how well a CPU and GPU will work together and then look at real-world benchmark data to make the right decision. Bottleneck calculators like the one from PC Builds let you pick the resolution and choose between general, CPU-, and GPU-bound tasks. Games, video editing, and machine learning tasks all rely on the GPU, so pick GPU-intensive tasks.
For example, I picked a combination of CPU and GPU that I know works well based on a CPU comparison video by _Legit Camel Retro_—the AMD Ryzen 5600 and the NVIDIA RTX 3060 Ti . Both were on the lower end of the mid-range lineups at the time of release. PC Builds’ bottleneck calculator gave me a 6.4% processor bottleneck, which means I could squeeze out a few more FPS if I got a better CPU, which is true but also not something I should worry about.
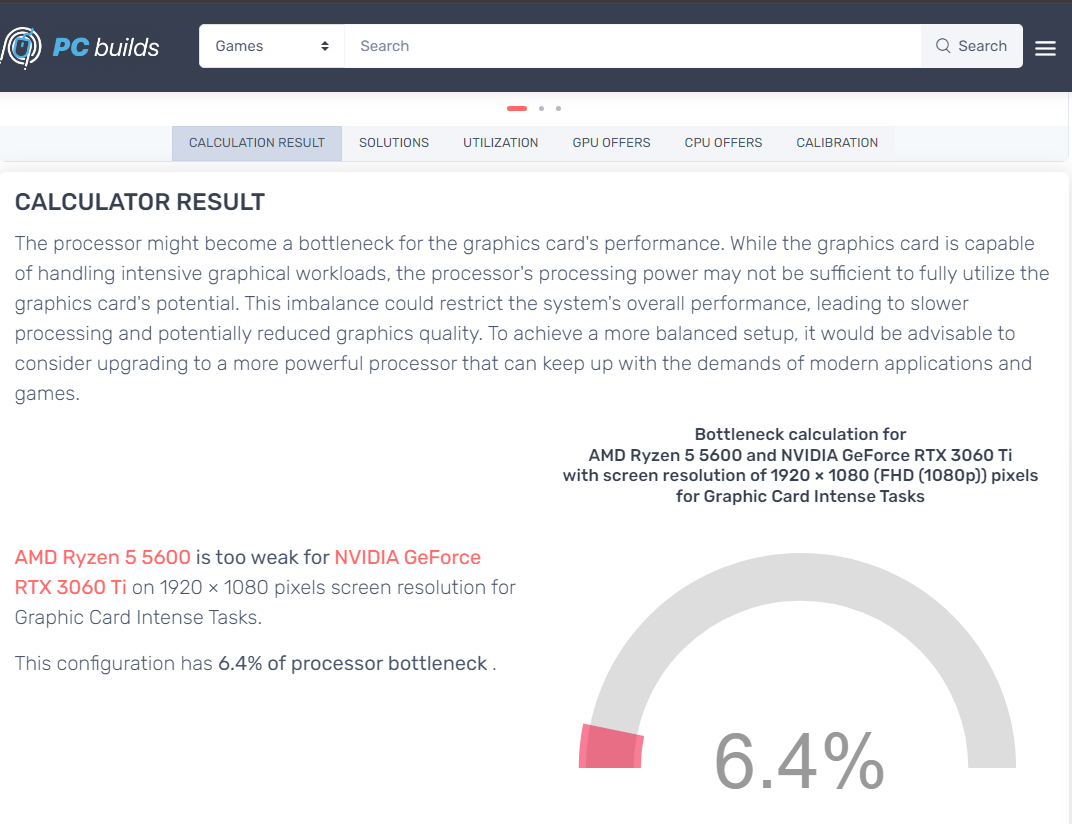
PC Builds
While I can’t fully trust the 6.4% figure, I know that this combination of hardware would be reasonable. Let’s stick with our Ryzen 5 5600 and 1080p, but swap out the graphics card for something way more powerful—the mighty NVIDIA RTX 4080 . This time, I got a 31% CPU bottleneck, which is less than what Hardware Unboxed got for their 1080p and even 1440p tests. I calculated the bottleneck percentage based on their average FPS scores for the Ryzen 5 5600 and Ryzen 7 7800X3D and got 53.28% and 40.63% for 1080p and 1440p, respectively.
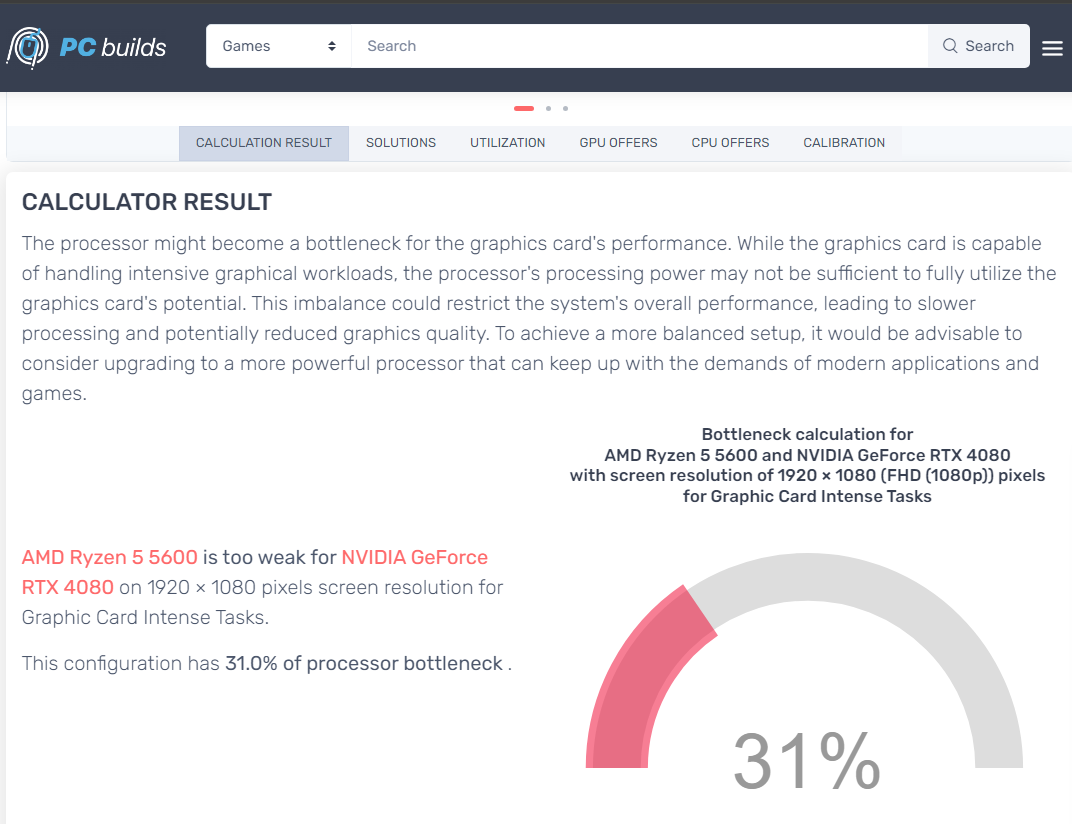
PC Builds
Nonetheless, the bottleneck calculator showed a significant percentage that’d make you reconsider your combination. Bottleneck scores below 7–8% shouldn’t be much of a concern, but if the score is above 10%, you should probably consider a different hardware combination.
Bottleneck calculators are an excellent starting point for your build because they make it easy to combine any CPU and GPU model. Still, you should check performance benchmarks and hardware reviews to make sure the performance aligns with what the calculator shows.
Also read:
- [Updated] 2024 Approved Enhancing Productivity The Art of Using No-Cost Timers
- [Updated] 2024 Approved Ideal Matches Free & Paid Ultra HD Playback Tools for Windows, macOS
- [Updated] In 2024, Edit Your Way to Success IOS/Android Apps for YouTube Shorts
- [Updated] Quick & Easy Xbox One Image Snaps for Gaming for 2024
- 2024 Approved The Real-World Usability of Photoshop’s Motion Reduction
- Enabling Smooth Transitions with Revived FreeSync
- Fraps Your Go-To Screen Recorder, In 2024
- GoPro Vs. Polaroid Which Video Editor Prevails?
- The Indispensability of the Camera Hump on Phones: Why Compromise Is Not an Option
- The Ultimate Guide to the Top Boombox Models
- Top 5 Car Locator Apps for Motorola Moto G84 5G | Dr.fone
- Top-Rated PC Liquid Coolers: Optimize Your System's Performance
- Top-Rated Smart Lighting Solutions
- Travel-Friendly Bluetooth Audio System - Your Ultimate Companion for Easy Journeys
- Troubleshooting Launchpad: Resolving Mac Boot Issues via Recovery Options
- Ultimate Guide to NuPhy Air75 V2: Why Every Mac Enthusiast Needs This Mechanical Masterpiece
- Understanding Wi-Fi Signal Enhancers: Extenders, Boosters & Repeaters Explained
- Title: Why Bottleneck Estimators May Lack Precision: My Reasons for Continuing Their Use
- Author: Richard
- Created at : 2024-12-06 19:12:53
- Updated at : 2024-12-12 16:45:02
- Link: https://hardware-updates.techidaily.com/why-bottleneck-estimators-may-lack-precision-my-reasons-for-continuing-their-use/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.